Snowflake’s Data Cloud is powered by an advanced data platform provided as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Snowflake enables data storage, processing, and analytic solutions that are faster, easier to use, and far more flexible than traditional offerings.
The Snowflake data platform is not built on any existing database technology or “big data” software platforms such as Hadoop. Instead, Snowflake combines a completely new SQL query engine with an innovative architecture natively designed for the cloud. To the user, Snowflake provides all of the functionality of an enterprise analytic database, along with many additional special features and unique capabilities.
In this Topic:
Data Platform as a Cloud Service
Snowflake is a true SaaS offering. More specifically:
There is no hardware (virtual or physical) to select, install, configure, or manage.
There is virtually no software to install, configure, or manage.
Ongoing maintenance, management, upgrades, and tuning are handled by Snowflake.
Snowflake runs completely on cloud infrastructure. All components of Snowflake’s service (other than optional command line clients, drivers, and connectors), run in public cloud infrastructures.
Snowflake uses virtual compute instances for its compute needs and a storage service for persistent storage of data. Snowflake cannot be run on private cloud infrastructures (on-premises or hosted).
Snowflake is not a packaged software offering that can be installed by a user. Snowflake manages all aspects of software installation and updates.
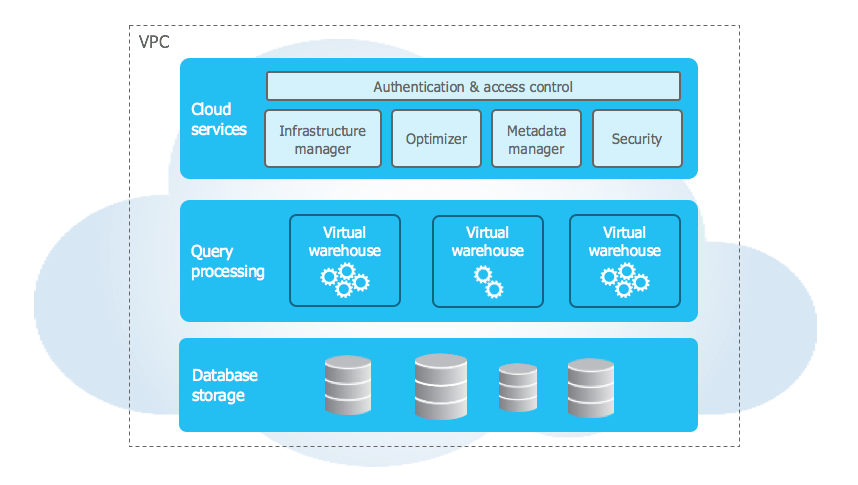
Snowflake Architecture
Snowflake’s architecture is a hybrid of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing database architectures. Similar to shared-disk architectures, Snowflake uses a central data repository for persisted data that is accessible from all compute nodes in the platform. But similar to shared-nothing architectures, Snowflake processes queries using MPP (massively parallel processing) compute clusters where each node in the cluster stores a portion of the entire data set locally. This approach offers the data management simplicity of a shared-disk architecture, but with the performance and scale-out benefits of a shared-nothing architecture.
Snowflake’s unique architecture consists of three key layers:
Database Storage
When data is loaded into Snowflake, Snowflake reorganizes that data into its internal optimized, compressed, columnar format. Snowflake stores this optimized data in cloud storage.
Snowflake manages all aspects of how this data is stored — the organization, file size, structure, compression, metadata, statistics, and other aspects of data storage are handled by Snowflake. The data objects stored by Snowflake are not directly visible nor accessible by customers; they are only accessible through SQL query operations run using Snowflake.
Query Processing
Query execution is performed in the processing layer. Snowflake processes queries using “virtual warehouses”. Each virtual warehouse is an MPP compute cluster composed of multiple compute nodes allocated by Snowflake from a cloud provider.
Each virtual warehouse is an independent compute cluster that does not share compute resources with other virtual warehouses. As a result, each virtual warehouse has no impact on the performance of other virtual warehouses.
For more information, see Virtual Warehouses.
Cloud Services
The cloud services layer is a collection of services that coordinate activities across Snowflake. These services tie together all of the different components of Snowflake in order to process user requests, from login to query dispatch. The cloud services layer also runs on compute instances provisioned by Snowflake from the cloud provider.
Services managed in this layer include:
Authentication
Infrastructure management
Metadata management
Query parsing and optimization
Access control
Connecting to Snowflake
Snowflake supports multiple ways of connecting to the service:
A web-based user interface from which all aspects of managing and using Snowflake can be accessed.
Command line clients (e.g. SnowSQL) which can also access all aspects of managing and using Snowflake.
ODBC and JDBC drivers that can be used by other applications (e.g. Tableau) to connect to Snowflake.
Native connectors (e.g. Python, Spark) that can be used to develop applications for connecting to Snowflake.
Third-party connectors that can be used to connect applications such as ETL tools (e.g. Informatica) and BI tools (e.g. ThoughtSpot) to Snowflake.
Comments
Post a Comment